Imf Lending Crisis
crisis lending wallpaperThe fund will extend. Fiscal measures so far have amounted to about 8 trillion and central banks have undertaken massive in some cases unlimited liquidity injections.
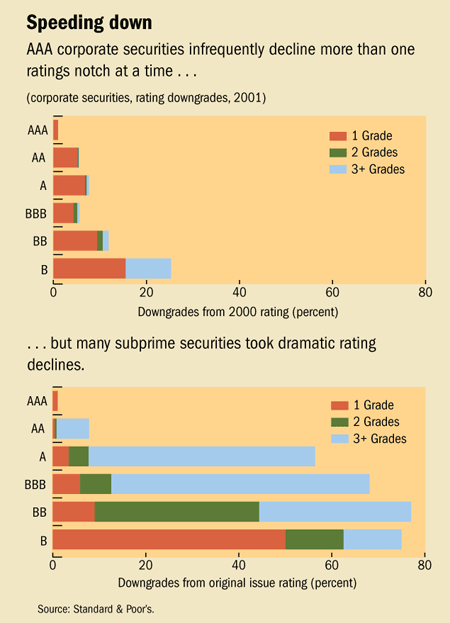 Finance Development June 2008 Outbreak U S Subprime Contagion
Finance Development June 2008 Outbreak U S Subprime Contagion
Thomas Reichmann and Carlos de Resende.
Imf lending crisis. IMF COVID-19 Hub All the information on the IMFs response to the crisis. The IMF is forecasting that the global economy will shrink by 3 this year the worst downturn since the 1930s and far more severe than the 2008 financial crisis. A member countrythere are 189 members as of 2020typically summons the IMF when it can no longer finance imports or service its debt to creditors a sign of potential crisis.
The 1976 UK Sterling Crisis was a balance of payments or currency crisis in the United Kingdom in 1976 which forced James Callaghans Labour government to borrow 39 billion 175 billion in 2019 from the International Monetary Fund IMF at the time the largest loan ever to have been requested from the IMF. This page provides an overview of assistance approved by the IMFs Executive Board since late March 2020 under its various lending facilities and debt service relief financed by the Catastrophe Containment and Relief Trust CCRT. The IMFs Lending Toolkit and the Global Financial Crisis Series Number.
These timely actions helped maintain the IMFs 1 trillion lending capacity so it can provide strong support as countries face unprecedented financing needs resulting from the pandemic. A Review of Crisis Management Programs Supported by IMF Stand-By Arrangements 200811 Series Number. The IMFs lending toolkit is continuously refined to meet countries changing needs.
The IMF is forecasting that the global economy will shrink by 3 this year the worst downturn since the 1930s and far more severe than the 2008 financial crisis. He IMF assists countries hit by crises by providing them financial support to create breathing room as they implement adjustment policies to restore economic stability and growth. Since the beginning of the COVID-19 crisis the IMF has provided emergency financing to 80 countries drawing on the GRA and PRGT for the most recent data please see the IMFs COVID-19 Financial Assistance and Debt Service Relief Tracker.
Both the IMF and the World Bank. Overall the IMF is currently making about 250 billion a quarter of its 1 trillion lending capacity available to member countries. If the objective underlying the bailout was.
We propose a five-step plan that ensures sufficient resources are available to meet a high. IMF loans are meant to help member countries tackle balance of payments problems stabilize their economies and restore sustainable economic growth. But in 2008 the IMF began making loans to countries hit by the global financial crisis The IMF currently has programs with more than 50 countries around the world and has committed more than 325 billion in resources to its member countries since the start of the global financial crisis.
For our part the IMF has 1 trillion lending capacity4 times more than at the outset of the Global Financial Crisisat the service of its 189 member countries. WASHINGTON AP The head of the International Monetary Fund said Wednesday that the lending agency is facing huge demand for support from its members during the global pandemic. How the IMF Bungled the Greek Debt Crisis Greeces public debt which was 120 of the GDP when the IMF undertook the rescue has since risen to 170.
Overall since May 1 2019 the IMF has approved about 165 billion in loans including those predating the pandemic. The IMFs twice-yearly World Economic Outlook was prepared for this weeks spring meetings of the 189-nation IMF and its sister lending organization the World Bank. It also provides precautionary financing to help prevent and insure against crises.
While the financial crisis has sparked renewed demand for IMF financing the decline in lending that preceded the financial crisis also reflected a need to adapt the IMFs lending instruments to the. The IMF has responded to the COVID-19 crisis by quickly deploying financial assistance developing policy advice and creating special tools to assist member countries. As global leaders begin to put together an international financing package to help low-income countries LICs recover from the COVID-19 crisis they are looking to the International Monetary Fund IMF to be a critical financial and policy anchor for LICs sustainable economic recovery.
This crisis resolution role is at the core of IMF lending. At the same time the global financial crisis has highlighted the need for effective global financial safety nets to help countries cope with adverse shocks. Much of this was provided under emergency financing instruments designed to help countries with urgent balance of payments needs.